What Is Bitumen? Meaning, Uses, Road Construction & Waterproofing Guide
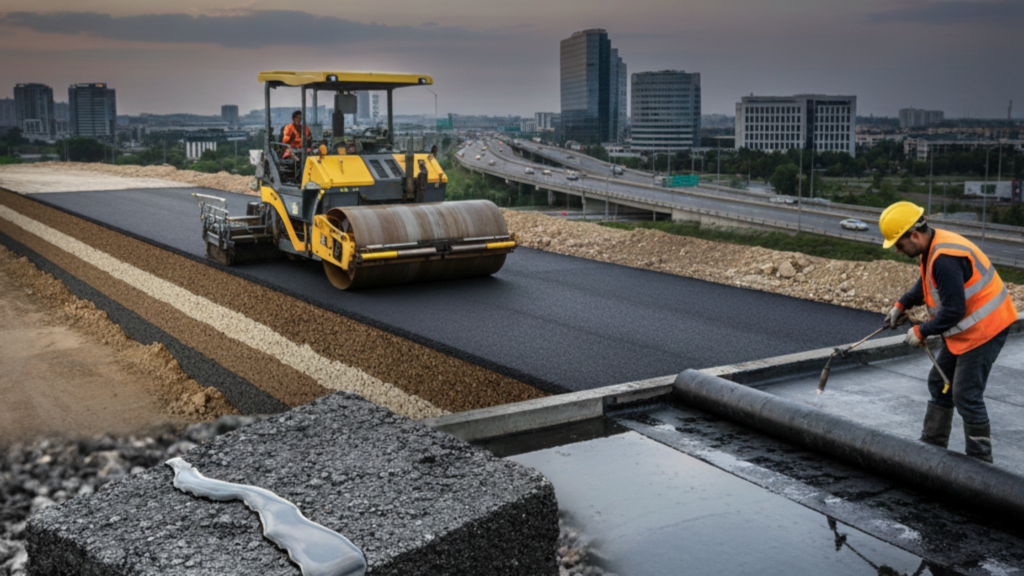

What is a bitumen and why is it among the most common materials in the contemporary construction? Bitumen is an important aspect of infrastructure development particularly on highways and urban roads as well as on roofs and other basement areas.
Bitumen, asphalt and tar are some of the terms that many individuals use interchangeably. As a matter of fact, the purpose of each of them is different.
The knowledge on the meaning, definition, uses, benefits, restrictions and comparison of bitumen with asphalt enables engineers, constructors, contractors and purchasers to make better decisions.
What Is Bitumen? (Meaning & Definition)

Bitumen Meaning
The bitumen meaning is a black, sticky and highly viscous substance derived out of crude oil. It is primarily utilized as an adhesive and water resistant construction product.
Simply, bitumen is the paste that has a binding effect on the road substance and keeps water out of structures.
Bitumen Definition
Bitumen can be characterised as a mixture of petroleum-based hydrocarbons that is semi solid or liquid at normal temperatures and is commonly used in road construction, water proofing and industrial purposes.
Bitumen is one of the most dependable kinds of construction materials due to its high water resistant and sticking properties.
Bituminous Meaning Explained
Bituminous can be used to refer to something that holds, is composed of, or to do with bitumen.
Common examples include:
- Bituminous road
- Bituminous waterproofing membrane
- Bituminous coating
Anything described as bituminous uses bitumen as a key component.
How to Pronounce Bitumen
Many users search for bitumen pronunciation.
- British pronunciation: BIH-chyuh-men
- American pronunciation: bi-TOO-men
This answers:
- how to pronounce bitumen
- pronounce bitumen
- pronunciation of bitumen
Uses of Bitumen
Common Uses of Bitumen
Bitumen uses are distributed across numerous industries due to its flexibility, durability and the ability to stay waterproof.
Major uses of bitumen include:
- Road construction and highways
- Waterproofing systems
- Roofing sheets
- Pavements and airport runways
- Industrial coatings
In simple terms, bitumen is applied in the production of tough and durable surfaces with resistance to water.
Bitumen for Road Construction

Why Is Bitumen Used for Roads?
Bitumen for roads is preferred because it:
- Binds aggregates firmly
- Absorbs traffic stress
- Resists water penetration
- Performs well in varying temperatures
- Facilitates repairs and maintenance.
It renders the bituminous roads economical and lifespan.
Bituminous Road Construction Process
A bituminous road is built in layers:
- Subgrade (natural soil)
- Granular sub-base
- Bituminous base layer
- Bituminous wearing course
Bitumen is used as the binding agent the one that glues aggregates in place to provide roads with flexibility and strength.
Bitumen vs Asphalt: Are They the Same?

Are Bitumen and Asphalt the Same?
Bitumen and asphalt are not similar but rather close to each other.
- Bitumen → A binding material obtained from crude oil
- Asphalt → A mixture of bitumen + aggregates (stone, sand, gravel)
👉 Bitumen is the starting material, asphalt is the end product.
Difference Between Asphalt and Bitumen
| Feature | Bitumen | Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Binder | Finished road material |
| Composition | Hydrocarbon binder | Bitumen + aggregates |
| Usage | Waterproofing & binding | Road surfacing |
| Traffic Load | Cannot handle alone | Designed for traffic |
Which Is Better: Bitumen or Asphalt?
It depends on the application.
- Bitumen is better for:
- Waterproofing
- Roofing
- Sealing and binding
- Asphalt is better for:
- Roads
- Driveways
- Pavements
One does not substitute the other- they complement each other.
Is Asphalt Better Than Bitumen?
As a road surface, yes.
As a raw material, no.
Bitumen cannot be utilized on its own because it cannot and will not carry off traffic loads; thus, it gets combined with aggregates to make asphalt.
Why Is Bitumen Not Used Alone?
Bitumen is not used alone because:
- It becomes soft at high temperatures
- It cannot bear heavy traffic loads
- It becomes sticky and deforms easily
That’s why aggregates are added to create asphalt.
Disadvantages and Problems of Bitumen
What Are the Disadvantages of Using Bitumen?
Some disadvantages of bitumen include:
- Temperature sensitivity
- Softening in extreme heat
- Brittleness in extreme cold
- Aging and oxidation over time
Modern construction minimizes these issues using polymer-modified bitumen (PMB).
What Are the Problems With Bitumen?
Common problems include:
- Rutting under heavy loads
- Cracking due to aging
- Oxidation over time
These are controlled through proper grade selection and design.
What Are the Dangers of Bitumen?
Potential risks include:
- Burns from hot bitumen
- Fumes during heating
- Environmental damage if spilled
Using protective gear and following safety standards reduces these risks.
Bitumen, Asphalt & Safety Myths
Does Oil-Based Bitumen Contain Asbestos?
No.
Contemporary bitumen is not mixed with asbestos. In the current bitumen products, asbestos is prohibited.
Why Is Bitumen Not Used as Fuel?
Bitumen is:
- Too heavy
- Too viscous
- Inefficient for burning
It is better suited for binding and waterproofing, not fuel.
Bitumen Waterproofing Explained
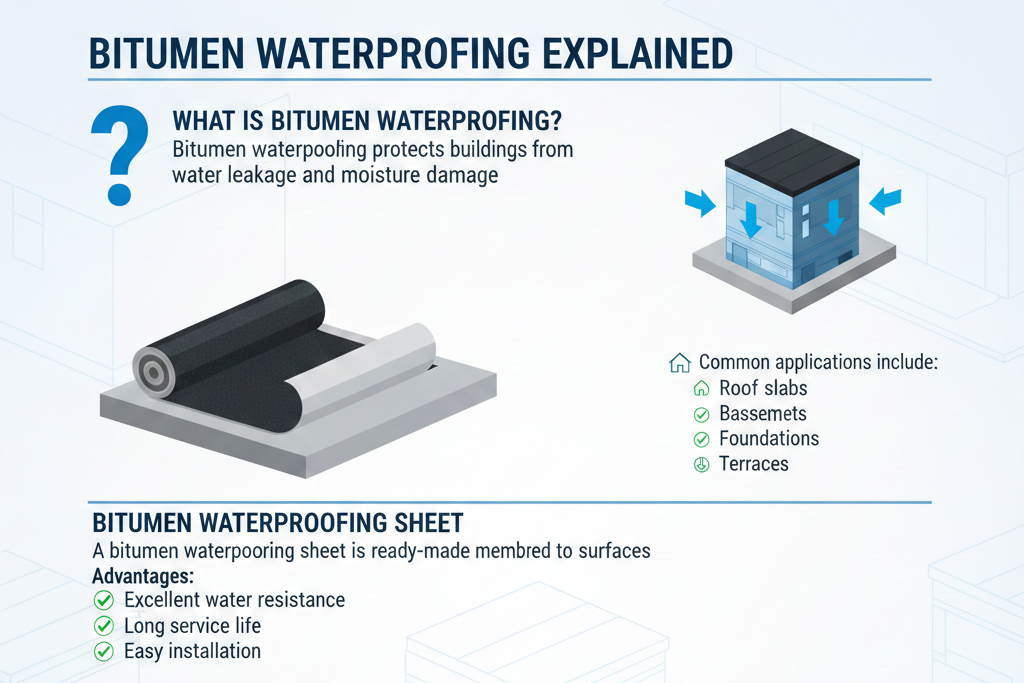
What Is Bitumen Waterproofing?
Bitumen waterproofing protects buildings from water leakage and moisture damage.
Common applications include:
- Roof slabs
- Basements
- Foundations
- Terraces
Bitumen Waterproofing Sheet
A bitumen waterproofing sheet is a ready-made membrane applied to surfaces.
Advantages:
- Excellent water resistance
- Long service life
- Easy installation
Bituminous Membrane
A bituminous membrane is a flexible waterproofing layer used for:
- Roofs
- Underground structures
- Industrial buildings
Bitumen Roofing Sheets
Bitumen roofing sheet has broad application in:
- Warehouses
- Factories
- Commercial buildings
They provide:
- Waterproofing
- UV resistance
- Thermal stability
Pricing & Cost Insights
Bitumen Price in India
Bitumen price in India depends on:
- Grade (VG-10, VG-30, VG-40)
- Crude oil prices
- Location and quantity
Common search queries include:
- bitumen price
- bitumen rate today
- bitumen price per kg
- bitumen VG-30 price today
- road tar price
The prices fluctuate, hence always ask suppliers.
Substitutes & Alternatives
Is There Anything Better Than Asphalt?
Alternatives include:
- Concrete (long life, higher cost)
- Paver blocks (decorative)
- Gravel (low traffic areas)
However, asphalt remains the most flexible and repair-friendly option.
What Is a Substitute for Bitumen?
Possible substitutes:
- Bio-bitumen
- Polymer binders
- Cement concrete (for some uses)
Nevertheless, bitumen is the cheapest alternative.
Common Questions Answered (FAQs)
What Is the Black Stuff they Spray on Roads?
It is asphalt, made using bitumen and aggregates.
Is Asphalt Cement the Same as Bitumen?
Yes. Bitumen, which is also known as asphalt cement is primarily used in USA.
What Is Asphalt Cement?
Pure refined bitumen used to bind aggregates.
What Is Another Name for Bitumen?
- Asphalt binder
- Asphalt cement
- Road bitumen
What Are the 4 Types of Bitumen?
- Penetration grade bitumen
- Viscosity grade bitumen
- Cutback bitumen
- Bitumen emulsion
What Is Poor Man’s Concrete?
Poor man asphalt is said to be the poor man concrete since it is cheaper, faster to be laid and it is also easy to repair.
Conclusion
Bitumen is also one of the backbone materials of modern infrastructure and usually utilized in the roads, waterproofing and roofing.
The knowledge of the meaning of bitumen, its applications, constraints and the difference between asphalt and bitumen are useful in the selection of the appropriate construction solution.
Bitumen can be combined with aggregates to produce asphalt, which is one of the most trusted and commonly used materials of road-building in the world.
