Hydrochloric Acid (HCL): Formula, Uses, Properties, Safety & Industrial Applications
Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) is one of the most popular, and important inorganic acids in the world.
Hydrochloric acid is a very necessary substance which is applied in the heavy industries, water treatment plants, laboratories and even the human digestive system.
HCL is very significant chemical in most industries as it is a strong acidic material, which is highly reactive and versatile.
It is a full-fledged manual on hydrochloric acid regarding learning about the chemical formula, chemical properties, industrial usage, safety precautions and commercial usage of the product.
What is Hydrochloric Acid (HCL)?
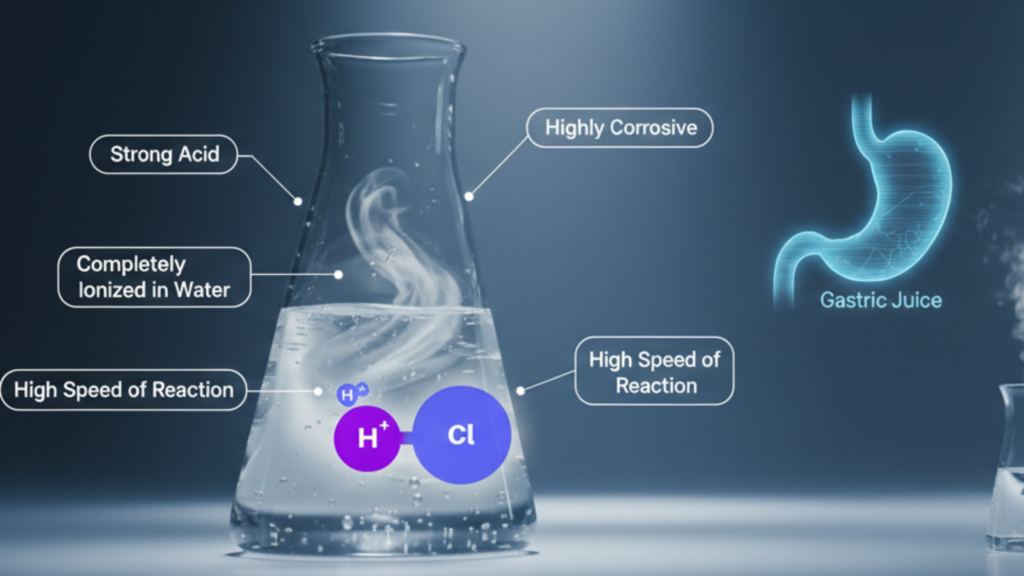
Hydrochloric acid is an inorganic acid which is very strong, colorless and is formed when hydrogen chloride gas (HCl) is dissolved in water.
In a water solution, it dissociates all the way into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻). This makes it act strongly as an acid.
The gastric juice is made in the stomach of a human being and also the hydrochloric acid is made in large scale at an industrial level where it can be utilized in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry as well as in the water treatment industry.
Key characteristics:
- Strong acid
- Highly corrosive
- Completely ionized in water
- High speed of response to metals and bases.
Chemical Name, Formula & Molecular Structure
- Chemical Name: Hydrochloric Acid
- Chemical Formula: HCl
- Molecular Formula: HCl
- Molar Mass: 36.46 g/mol
Structure Explanation
Hydrochloric acid comprises of one covalent bond between hydrogen and chlorine.
At the time of dissolution in water, this bond rupture produces hydrogen (H₃O⁺) and chloride (Cl⁻) ions that makes it highly acidic.
Hydrogen Chloride vs Hydrochloric Acid
- Hydrogen Chloride (HCl): Gas form
- Hydrochloric Acid: Aqueous solution of HCl
This difference is essential in industrial manipulation and chemical reaction.
Physical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Odor | Sharp, pungent |
| Density (37%) | ~1.18 g/ml |
| Boiling Point | ~110°C |
| Melting Point | −27°C |
| Solubility | Completely soluble in water |
| pH (Concentrated) | 0–1 |
Chemical Properties of Hydrochloric Acid
- Powerful acid which is wholly dissociated in water.
- Combines violently with metals to form hydrogen gas.
- Neutralizes bases to form salts and water
- Reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to release CO₂
- Non-oxidizing acid
pH Value of Hydrochloric Acid
PH of the hydrochloric acid varies with concentration:
- Concentrated HCL: pH ≈ 0–1
- Diluted HCL: pH increases proportionally with dilution
Hydrochloric acid is extremely corrosive because of its low pH hence it should be handled carefully.
Industrial Uses of Hydrochloric Acid
a) Steel & Metal Industry
- Pickling of steel in order to cut off rust and oxide scale.
- Preparation of the surface prior to the application of galvanizing or coating.
b) Chemical Manufacturing
- Chlorides (calcium chloride, ferric chloride) production.
- In the middle of organic and inorganic formation.
c) Water & Wastewater Treatment
- pH correction
- Ion-exchange resins Regeneration.
- Alkaline effluents neutralization.
d) Oil & Gas Industry
- Acidizing of oil wells
- Removal of carbonate deposits
Uses in Food & Pharmaceutical Industry
- pH regulation in food processing (as per regulatory limits)
- Manufacturing of pharmaceutical intermediates
- Production of APIs
- Processing equipment Cleaning and sterilization.
Laboratory & Commercial Cleaning Applications
- In laboratories, analytical reagent is used.
- Descaling agent
- Concrete and tile cleaning
- Maintenance of pool (muriatic acid).
Role of Hydrochloric Acid in the Human Stomach
Hydrochloric acid is secreted by parietal cells in the stomach lining.
Functions:
- Breaks down proteins
- Activates pepsinogen into pepsin
- Destroys harmful microorganisms
- Maintains acidic gastric pH (1–3)
Medical Disclaimer: Qualified medical personnel should be able to diagnose and treat digestive disorders.
Hazards & Health Effects
Hydrochloric acid is classified as a corrosive substance.
Potential Hazards:
- Severe skin burns
- Eye damage
- Respiratory tract irritation
- Corrosion of metals
Effects of Hydrochloric Acid on Skin
Exposure may cause:
- Redness and pain
- Chemical burns
- Blistering
First Aid:
- Immediately rinse under much water.
- Take off infected clothes.
- Consult a doctor in case of severe exposure.
Safety Guidelines, SDS & PPE
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Acid-resistant gloves
- Safety goggles
- Face shield
- Protective clothing
Storage & Handling:
- Keep in HDPE or corrosion-resistant containers.
- Store out of heat, metals and bases.
- Ensure proper ventilation
Hydrochloric Acid vs Muriatic Acid
| Aspect | Hydrochloric Acid | Muriatic Acid |
| Purity | High | Lower |
| Application | Industrial, pharma, lab | Cleaning, pools |
| Concentration | Controlled | Diluted |
Common Chemical Reactions
- Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
- Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂
- CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + CO₂ + H₂O
Manufacturing Process of Hydrochloric Acid
- Direct produces hydrogen and chlorine.
- Recovery of by-products of chlorination reactions.
- Absorption of HCl gas in water
Storage, Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- Store in labeled containers
- Neutralize before disposal
- Adhere to the environmental standards.
Grades of Hydrochloric Acid
- Industrial Grade
- Food Grade
- Laboratory Grade
- Pharmaceutical Grade
Commercial Importance & Supplier Selection
Such factors as buying hydrochloric acid include:
- Consistent concentration
- Quality certifications
- Safe packaging
- Reliable logistics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is hydrochloric acid flammable?
No, hydrochloric acid is non-flammable.
Is HCL a strong acid?
Yes, hydrochloric acid is a strong acid.
Is stomach acid hydrochloric acid?
Yes, gastric acid mainly contains hydrochloric acid.
What is hydrochloric acid (HCl) used for?
It is used in cleaning, metal processing, chemical manufacturing, and digestion in the stomach.
Are hydrochloric acid and HCl the same?
Yes, hydrochloric acid is the aqueous form of HCl.
Is HCl harmful?
Yes, concentrated HCl is corrosive and harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or touched.
Is HCl a type of salt?
No, HCl is an acid. Its salts are called chlorides.
What does HCl do for your body?
It helps digest food and kill bacteria in the stomach.
Is HCl a strong acid?
Yes, HCl is a strong acid.
Is HCl used for cleaning?
Yes, it is commonly used to remove rust, stains, and scale.
What happens when HCl mixes with water?
It releases heat and forms hydrochloric acid solution.
Where is HCl found in the body?
It is found in the stomach as gastric acid.
What does HCl smell like?
It has a strong, sharp, irritating smell.
Is HCl high risk?
Yes, in concentrated form it is high risk and corrosive.
What is HCl in medicine?
It is used to form drug salts for better absorption.
Which is the king of acid?
Sulfuric acid is commonly called the king of acids.
Why are so many drugs HCl?
HCl salts improve drug stability and absorption.
Is HCl a gas or liquid?
HCl is a gas; hydrochloric acid is its liquid solution.
What are the side effects of HCl?
Burns, irritation, breathing problems, and digestive damage.
What are the signs of too much acid in the body?
Heartburn, acidity, stomach pain, and acid reflux.
Can drinking water reduce stomach acid?
Yes, it can temporarily dilute stomach acid.
What is the highest hydrochloric acid?
Commercially, around 37% concentration.
Which acid is the strongest?
Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest known acid.
What is the weakest acid?
Hydrocyanic acid is considered very weak.
Can HCl clean a toilet?
Yes, it removes stains and limescale effectively.
What are 5 uses of HCl?
Cleaning, metal processing, food production, chemical manufacturing, and digestion.
Which food has hydrochloric acid?
No food contains HCl directly; it is produced in the stomach.
Conclusion
Hydrochloric acid (HCL) is a vital chemical with extensive industrial, laboratory, and biological importance. Although this is very effective due to its high acidity, it is very dangerous and strict measures must be taken.
Selecting the right grade and supplier who is reliable, is the sure way to achieve efficiency, safety and compliance throughout the applications.
