Water Treatment & Mining: Complete Guide to Processes, Technologies, and Industry Applications

Mining and water treatment are inseparable industries that are vital in the industry development, environmental conservation, and sustainability of the resources.
Mining processes involve the use of water at every level like during mining of minerals and processing of ore, dust control and cooling of the machines.
Concurrently, the mining activities produce complicated streams of wastewater that should be disposed of cautiously to avoid harm to the environment and to adhere to the regulations.
This is an all-encompassing guide explaining the process of water treatment and mining in detail covering definitions, treatment process, technology, chemicals, mining techniques, wastewater issues, and sustainable solutions applicable in the mining industry.
What Is Water Treatment?
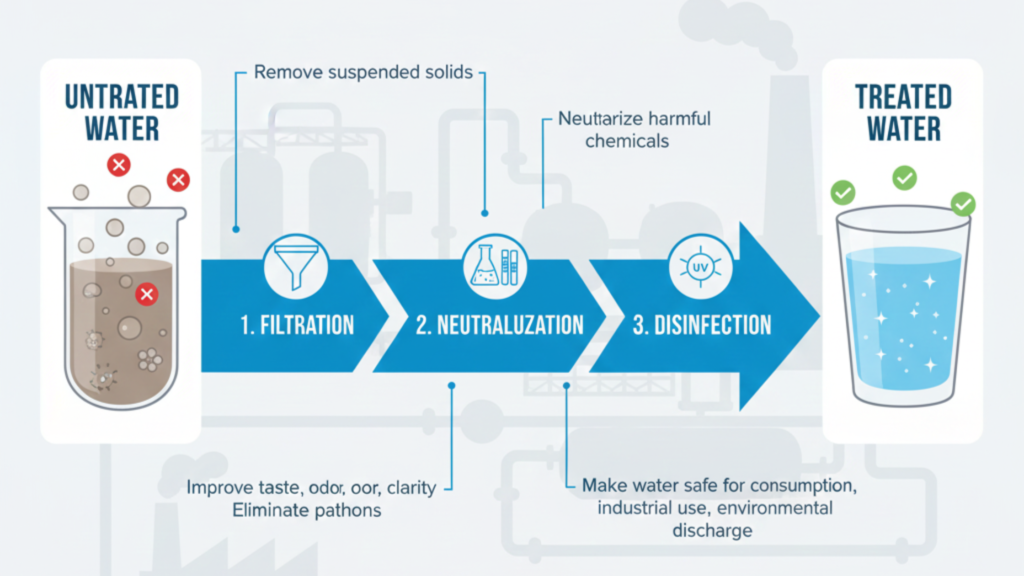
Treatment of water refers to the process of eliminating physical, chemical, and biological impurities in water to make it fit a particular purpose which may be drinking, use in an industry or to discharge safely to the environment.
Water Treatment Definition
The term water treatment is used to denote a combination of engineered processes that are aimed at:
- Remove suspended solids
- Neutralize harmful chemicals
- Eliminate pathogens
- Improve taste, odor, and clarity
- Make water safe for consumption, industrial use, or environmental discharge
Public health and industrial productivity as well as environmental protection depend on water treatment.
Why Water Treatment Is Important
The water needs to be treated since untreated water can:
- Carry harmful microorganisms
- Contain toxic metals and chemicals
- Damage industrial equipment
- Pollute rivers, lakes, and groundwater
- Violate environmental regulations
In other sectors like mining, failure to treat water properly may result in serious ecological damages, fines and closure of businesses.
Types of Water Treatment
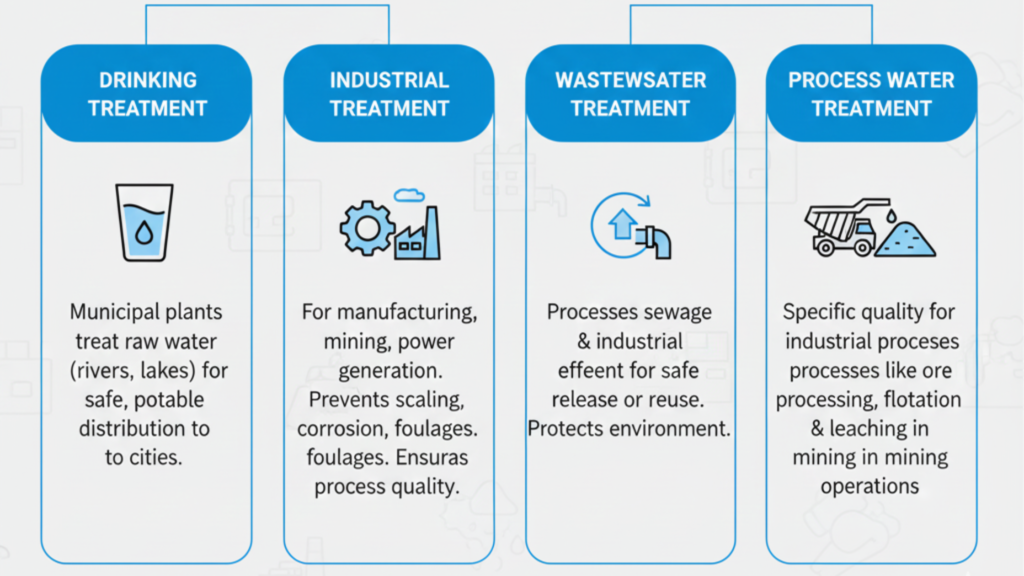
Various applications need different water treatment systems which are intended to achieve different water quality objectives.
Drinking Water Treatment
The raw water is treated by municipal water treatment plants and the potable water is distributed in city and town drinking systems.
Municipal Water Treatment
Municipal water treatment plants take the raw water in rivers, lakes, or reservoirs, and distribute it to cities and towns in potable form using a public distribution network.
Industrial Water Treatment
Application in industries, mining, power generation, chemicals, and manufacturing are some of the industries where industrial water treatment is applied. It maintains the process requirement of water and eliminates scaling, corrosion, and foulages.
Wastewater Treatment
Treatment of wastewater entails processing sewage and industrial effluid in order to allow reuse or to release the effluents safely into the environment.
Process Water Treatment
The water obtained through process water treatment is of a certain quality needed in industrial processes like ore processing, flotation and leaching in the mining.
Water Treatment Process Explained Step by Step
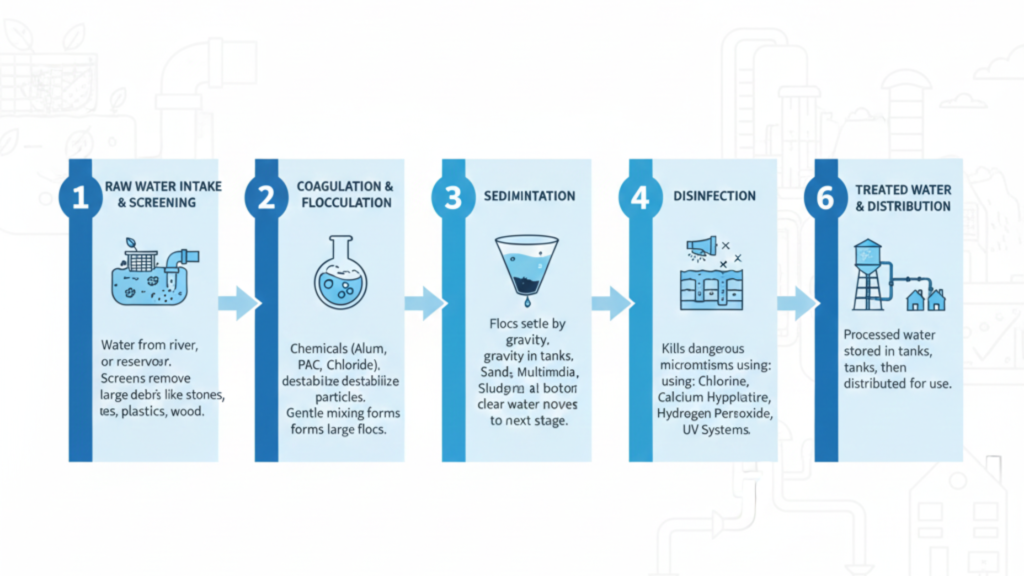
An average water treatment process entails the following stages:
1. Raw Water Intake and Screening
Raw water is gathered somewhere like a river, borewell or a reservoir. To prevent the destruction of downstream equipment, screening systems are used to eliminate huge debris such as stones, plastics, and leaves, as well as wood.
2. Coagulation and Flocculation
Aluminium Sulphate, Ferric Chloride or Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) are used as coagulants to destabilize the suspended particles. The water is very tenderly mixed by flocculation into large particles known as flocs.
3. Sedimentation
Flocs are removed by gravity in sedimentation tanks and a sludge is formed at the bottom. Crystal clear water remains in the next stage.
4. Filtration
Remaining fine particles are removed with the help of filtration by:
- Sand filters
- Multimedia filters
- Activated carbon filters
- Membrane filtration systems
5. Disinfection
Disinfection is done to kill microorganisms that are dangerous by using:
- Calcium Hypochlorite
- Chlorine
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- UV disinfection systems
6. Treated Water Storage and Distribution
Processing water is also stored in tanks and the treated water is given out to drink, industrial or reuse purposes.
How Does a Water Treatment Plant Work
A water treatment plant consists of a number of units which work together with each other:
- Raw water intake system
- Chemical dosing system
- Clarifiers
- Filters
- Disinfection units
- Treated water storage tanks
Safety and compliance are required through proper design of the plant, safe chemical storage rooms and controlled access keys.
Methods of Water Treatment
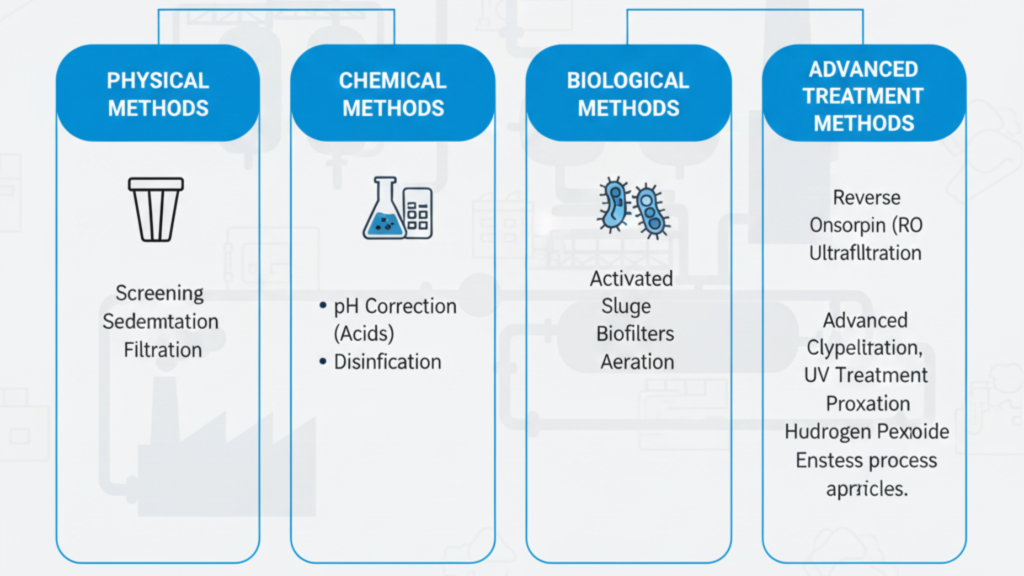
Physical Methods
- Screening
- Sedimentation
- Filtration
Chemical Methods
- Coagulation
- pH correction using acids
- Disinfection
Biological Methods
- Activated sludge process
- Biofilters
- Aeration
Advanced Treatment Methods
- Reverse Osmosis (RO)
- Ultrafiltration
- UV treatment
- Advanced oxidation processes
Chemicals Used in Water Treatment
The influence of treatment chemicals on water is extremely great in the purification and efficiency of the processes.
Common Water Treatment Chemicals

- Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) – pH regulating and cleaning.
- Sulphuric Acid 98% – pH correction.
- Nitric Acid 61% / 68% – Equipment cleaning
- Poly Aluminium Chloride (PAC) – Coagulation
- Poly DADMAC Flocculation aid.
- Aluminium Chlorohydrate (ARCH) – Coagulant of high efficiency.
- Ferric Chloride (Anhydrous / Liquid) – Coagulation and phosphorus removal
- Ferrous Sulphate Heptahydrate – Heavy metal removal
- Aluminium Sulphate – Clarification
- Calcium Hypochlorite 65% – Disinfection
- Hydrogen Peroxide (H₂O₂) 35% / 50% – Oxidation and odor control
Defoamers Used in Water Treatment
People can be affected by foaming and upset the therapeutic procedure. Foam is suppressed by defoamers.
Types of Defoamers
- Silicone-based defoamers
- Mineral oil-based defoamers
- Non-silicone defoamers
- Glycol-based defoamers
- Alcohol-based defoamers
- Food-grade defoamers
- Fatty acid-based defoamers
- Water-based defoamers
Drinking Water Treatment Process
The drinking water treatment process is centered towards safety and health to the people:
- Coagulation and sedimentation
- Filtration
- Disinfection
- Quality testing and monitoring
Difference Between Water Treatment and Water Purification
| Water Treatment | Water Purification |
|---|---|
| Improves water quality | Makes water ultra-pure |
| Used in municipal & industrial systems | Used for drinking or laboratories |
| Removes contaminants | Removes nearly all dissolved solids |
What Is Mining?

Mining refers to the extraction of valuable minerals, metals and other geological products in the earth as an economic and industrial resource.
The materials are vital in development of infrastructure, energy generation, production, construction, and technological development.
Raw materials that are mined include:
- Coal
- Iron ore
- Copper
- Gold
- Limestone
- Bauxite
- Rare earth minerals
Modern industries including power generation, steel production, electronics and construction industry would be impossible without mining.
Mining Definition
Mining is the process of digging, hacking, refining and processing of ores and minerals available in natural deposits under the surface or at the surface of the earth to use them in commerce and industries.
The mining process includes:
- Waste and tailings management
- Identification of mineral resources
- Safe extraction of ores
- Processing and beneficiation
History of Mining
Mining was a part of ancient civilization and has developed greatly over the years.
Early Mining
- Flint and obsidian mining was done in the Stone Age.
- Gold and copper were mined by ancient Egyptians.
- Romans introduced high underground mining methods.
Modern Mining
As a result of the industrial revolution, mining embraced:
- Heavy machinery
- Mechanized drilling
- Advanced blasting techniques
- Automation and digital monitoring systems
In the modern world, mining employs technology-enhanced and environmentally controlled methods that pay a lot of attention to the treatment of water, safety, and sustainability.
Types of Mining

The choice of mining techniques depends on the site, depth as well as the mineral deposit type.
Surface Mining
Surface mining is applied in case the deposit of minerals is near the surface.
Open-Pit Mining
- Large open excavation
- Ordinary to copper, iron ore, gold.
- Dust control and massive water management is required.
Strip Mining
- Applicable to coal and sedimentary formations.
- Includes the extraction of layers of soil (overburden)
Underground Mining
Applied when the deposits of the minerals are deep beneath the earth surface.
Shaft Mining
- Vertical shafts access depth ore bodies.
- Mandates water and mine water treatment.
Drift Mining
- Super horizontal tunnels into hills.
- Used for coal and metal ores
Other Mining Types
Placer Mining
- Extraction from riverbeds
- Common for gold and diamonds
In-Situ Mining
- Dissolved minerals at depths and pushed to the surface.
- Lower surface disturbance
Metal Mining
- Gold, copper, iron, zinc, lead
Mineral Mining
- Limestone, gypsum, phosphate, salt
Mining Process Explained

1. Exploration
- Geological surveys
- Core drilling
- Resource estimation
2. Site Development
- Land preparation
- Infrastructure development
- Water sourcing and drainage planning
3. Excavation
- Blasting
- Drilling
- Material handling
4. Ore Extraction
- Transportation of ore
- Crushing and grinding
5. Processing
- Flotation
- Leaching
- Gravity separation
6. Waste Management
- Tailings disposal
- Mine water treatment
- Environmental monitoring
Why Water Treatment Is Critical in Mining
Mining operations generate wastewater containing:
- Heavy metals
- Suspended solids
- Acids
- Process chemicals
Without proper treatment, mining wastewater can contaminate rivers, groundwater, and soil.
Mining Wastewater Treatment

Common Mining Water Issues
- Acid mine drainage
- Metal contamination
- High turbidity
Mining Wastewater Treatment Technologies
- Chemical precipitation
- Adsorption processes
- Membrane filtration
- Tailings water treatment
- Resource recovery techniques
Tailings Water Treatment
Tailings refer to the left-over after processing of ores. Tailings water should be treated in order to:
- Remove metals
- Reduce toxicity
- Enable water reuse
Water Treatment Plant in Mining Industry
A water treatment plant for mining ensures:
- Reuse of process water
- Environmental compliance
- Reduced freshwater consumption
- Sustainable mining operations
Water Neutrality in Mining and Industry
Water neutrality implies matching water abstraction with water replacement by reuse, recycling and conservation.
How Water Neutrality Is Achieved
- Zero Liquid Discharge systems
- Rainwater harvesting
- Treated wastewater reuse
- Efficient water management practices
Use of Treated Water in Corporate Campuses
The sewage treatment plants are associated with the use of treated water in:
- Gardening
- Cooling towers
- Toilet flushing
- Dust suppression
Big business corporations like IT campuses would use treated water and save fresh water to a large extent.
Water Treatment & Mining in India
The mining industry in India is dependent on effective water treatment to address the environmental regulations and sustainability requirements.
Mining companies are assisted by water treatment manufacturers and service providers in tailored treatment programs.
Choosing the Right Water Treatment Manufacturer
Key factors to consider:
- Industry experience
- Technical expertise
- Compliance with standards
- Reliable chemical supply
- After-sales support
Conclusion
In the contemporary industry, water treatment and mining cannot be separated. It is in the drinking water treatment through to highly complex mining wastewater management that the water treatment systems can be effective in protecting the environment, minimizing costs and long-term sustainability.
Through interventions such as providing advanced treatment technologies, quality chemicals, and knowledgeable working practices, industries are able to comply with regulatory standards, and in the process, the water resources are saved to be used by the future generations.
